
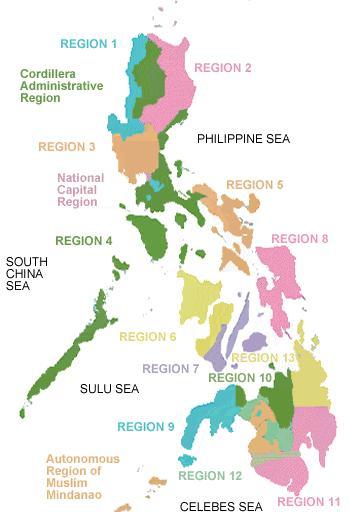
February 23, 1995: Region XIII ( Caraga) created and minor reorganization of some Mindanao regions.October 12, 1990: Executive Order 429 issued by President Corazon Aquino to reorganize the Mindanao regions but the reorganization never happened (possibly due to lack of government funds).Ratification rejected by residents in a plebiscite. October 23, 1989: First creation of Cordillera Autonomous Region.Region XII reverted to an administrative region. August 1, 1989: Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) created.July 15, 1987: Cordillera Administrative Region created.June 11, 1978: Regional center of Region IX transferred from Jolo, Sulu to Zamboanga City.June 2, 1978: Metropolitan Manila declared as the National Capital Region.November 7, 1975: Metropolitan Manila created.Minor reorganization of some Mindanao regions. August 21, 1975: Region IX divided into Sub-Region IX-A and Sub-Region IX-B.July 25, 1975: Regions IX and XII declared as Autonomous Regions in Western and Central Mindanao respectively.July 7, 1975: Region XII created and minor reorganization of some Mindanao regions.June 22, 1973: Pangasinan was transferred from Region III to Region I.Since that time, other regions have been created and some provinces have been transferred from one region to another. 1 as part of the Integrated Reorganization Plan of the former President Ferdinand Marcos. Regions first came to existence on September 24, 1972, when the provinces of the Philippines were organized into eleven regions under Presidential Decree No. Only one, the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, has an elected government and parliament to which the Congress of the Philippines has delegated certain powers and responsibilities. 16 of these are mere administrative groupings, each provided by the president of the Philippines with a regional development council (RDC) – in the case of the National Capital Region (Metro Manila), an additional metropolitan authority serves as the coordinating and policy-making body. Regional offices are usually but not necessarily located in the city designated as the regional center.Īs of 2019, the Philippines is divided into 17 regions. Most national government offices provide services through their regional branches instead of having direct provincial or city offices.
#MAP OF REGION X PHILIPPINES ISO#
Links to earthquake-related information for each state.In the Philippines, regions ( Filipino: rehiyon ISO 3166-2:PH) are administrative divisions that primarily serve to coordinate planning and organize national government services across multiple local government units (LGUs). Information by state, and world seismicity maps. Use real-time web services for your own applications. Get real-time earthquake notifications sent to you on your phone or by email, or subscribe to real-time feeds. Real-time Notifications, Feeds, and Web Services Various output formats, and links to earthquake details. View historic seismicity, find past earthquakes that meet your criteria. USGS and non-USGS collections of earthquake-related features and effects and shaking damage. Special Earthquakes, Earthquake Sequences, and Fault ZonesĬompilations of information about significant earthquakes, swarms or sequences, and fault zones of interest. Largest earthquakes, significant events, lists and maps by magnitude, by year, or by location. Tap/click on "gear icon" for options and settings. Photo by Peter Haeussler, USGS, November 9, 2002. Peter Haeussler prepares to measure the offset of a crevasse on the Canwell Glacier, Alaska, USA.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
